Week 2. Electric Organ Discharge
Contents
Week 2. Electric Organ Discharge¶
Some fish see and speak using electricity - behaviors termed electrosensation and electrocommunication. Mormyrids are a group of teleost fish with an electrocommunication system. You will use electrophysiology methods to eavesdrop on electric fish behavior.
Weakly electric fish essentially have a battery in their tail. It is made of modified muscle fibers, which means that it is innervated by motor neurons. Acetylcholine is released at this neuro-electric junction and, in response, the modified muscle fibers become polarized in parallel to produce a dipole-like electric field source.
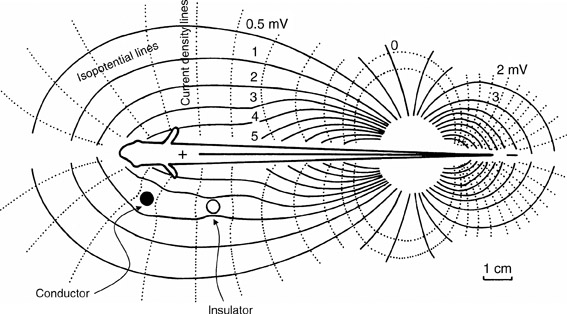
Therefore, when you place a pair of electrodes in the water near the fish, you can measure the voltage produced by the fish. Different species of fish polarize their batteries (the electric organ) with different timecourses. In other words, across time, the polarization waveform is species-specific.

Weakly electric fish use the electric field generated by their pulse-like electric organ discharges (EODs) to communicate with each other (electrocommunication and to sense the physical environment around them (via distortions of the electric field cause by the physical environment; electrolocation).

